Parker H. Holzer

parker.holzer@yale.edu
About Me CV Other Sites
Research Projects
Astrostatistics
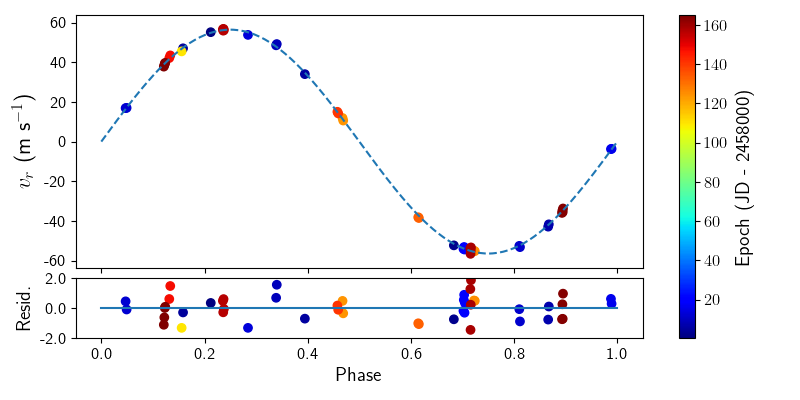
- A Hermite-Gaussian Based Radial Velocity Estimation Method: The radial velocity method is one of the techniques used to detect the signal of a planet orbiting a distant star by analyzing the light from that star. This project uses the Hermite-Gaussian functions to mathematically formulate the radial velocity method as weighted linear regression. This is shown through both simulation studies and analysis of real data to outperform the traditional cross-correlation function approach. Paper journal link R package Python source code
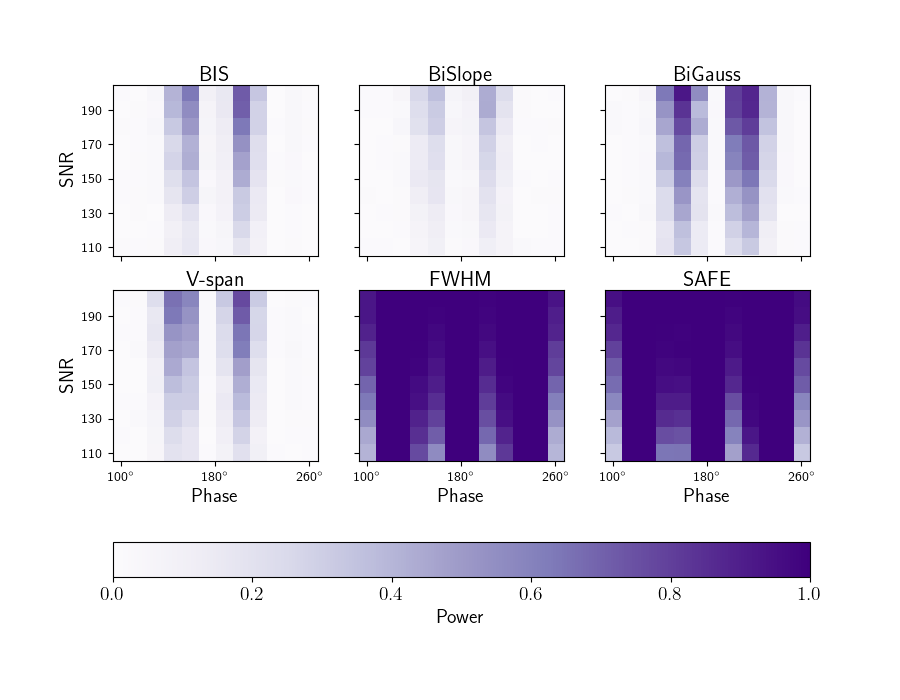
- A Stellar Activity F-statistic for Exoplanet Surveys (SAFE): In the radial velocity method for finding exoplanets, stellar activity in the atmosphere of the host star can distort the signal imposed by the orbiting planet. This project introduces a new statistic designed to detect the presence of such stellar activity. We demonstrate that this new F-statistic behaves as expected when no stellar activity is present, and has higher statistical power than many traditional stellar activity indicators designed for the same purpose. Paper journal link Python source code
Human Placenta
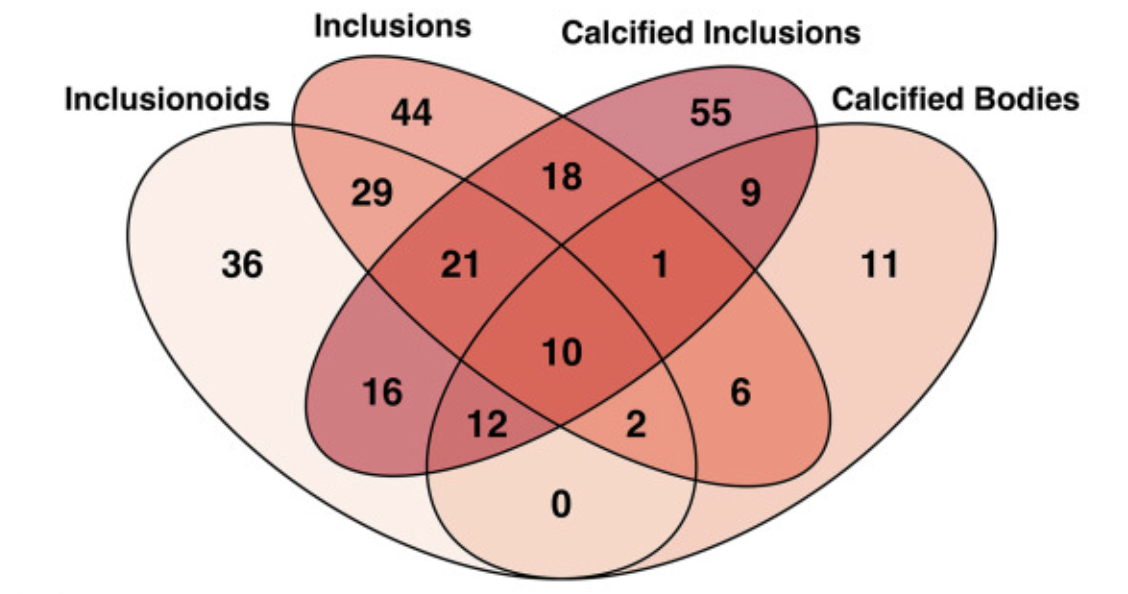
- Trophoblasst Inclusions in the Human Placenta: Identification, Characterization, Quantification, and Interrelations of Subtypes: Trophoblast inclusions are a feature that can occur on the human placenta during pregnancy. In this project I used statistical bootstrapping to demonstrate that the four subtypes of these inclusions have statistcally significant Spearman correlations with each other. Paper journal link
- Causes of Unexplained Pregnancy Loss: Ongoing project
- Genetics, Not the Uterine Environment, Drive the Formation of Trophoblast Inclusions: Insights From a Twin Study: In this study I derived and implemented a generalized likelihood ratio test for testing whether two samples of exponentially-distributed random variables have the same mean. Applying this to a study of monozygotic and dizygotic twins, we find that the trophoblast inclusion difference is greater for dizygotic twins than for monozygotic twins. Paper journal link (see Supplementary File in Appendix A)
Other Projects
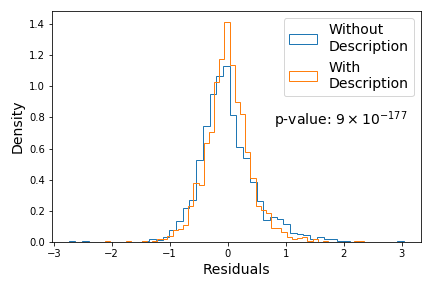
- Topic-Modeling of Connecticut House Descriptions: Ever wondered whether it’s worth reading over those lengthy descriptions on real estate websites when searching for a house to buy? Well, using topic-modeling on the house descriptions for a set of Connecticut houses listed for sale in early 2021 and plugging in the results to a linear model of the listing price with the living area, lot size, bedroom count, bathroom count, and year built, I find that the answer is ABSOLUTELY! With statistical significance (p-value < 0.00000001) including the (dimensionally-reduced) house descriptions is found to improve the prediction of the listing price by approximately 35%! So if you’re buying a house, don’t skip over the house descriptions. Python source code
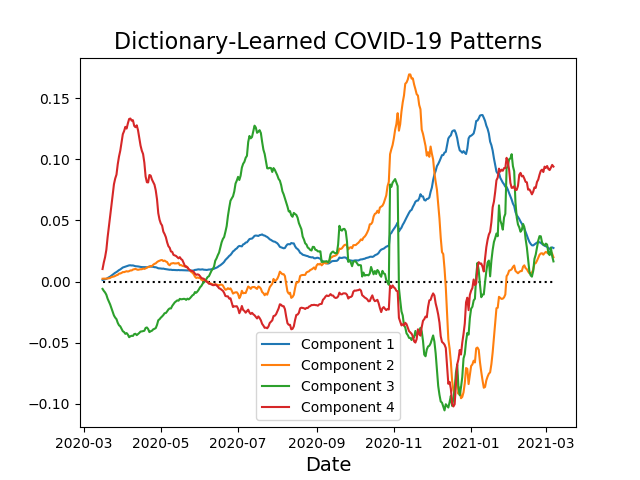
- COVID-19 Dictionary Learning: In this project I analyze the time series of positive cases for COVID-19 for each of the United States and territories using dictionary learning. Overall, approximately 95% of the data can be explained as a linear combination of four interpretable patterns, suggesting that the pandemic’s progression over time in the United States is actually rather straight-forward. Python source code
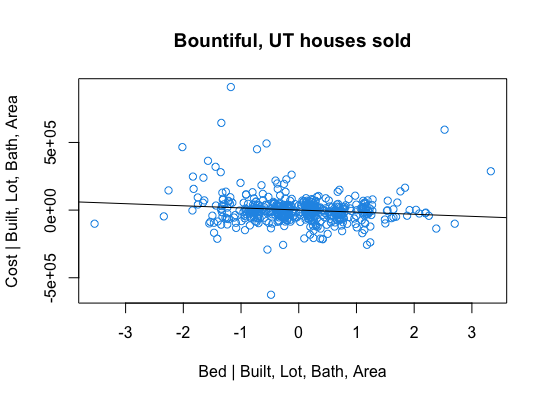
- Bountiful Real Estate Home Value Modeling: Here I use webscraping to obtain data on recently (as of March 2021) sold houses in Bountiful, Utah. Using multiple regression I demonstrate that after acconting for effects of lot size, year built, living area, and bathroom count, the value decreases by about $15,000 for each additional bedroom. Furthermore, I demonstrate that the value depends more quadratically than linearly on the living area. R source code